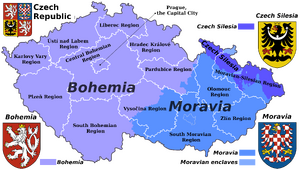
Moravia
| Author:Laxman Burdak, IFS (R) |
Moravia (मोराविया) is a historical country in the Czech Republic (forming its eastern part) and one of the historical Czech lands, together with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
Origin
Jat clans
History
Roman era: Around 60 BC, the Celtic Volcae people withdrew from the region and were succeeded by the Germanic Quadi. Some of the events of the Marcomannic Wars took place in Moravia in AD 169–180. After the war exposed the weakness of Rome's northern frontier, half of the Roman legions (16 out of 33) were stationed along the Danube. In response to increasing numbers of Germanic settlers in frontier regions like Pannonia, Dacia, Rome established two new frontier provinces on the left shore of the Danube, Marcomannia and Sarmatia, including today's Moravia and western Slovakia.
In the 2nd century AD, a Roman fortress[24][25] stood on the vineyards hill known as German: Burgstall and Czech: Hradisko ("hillfort"), situated above the former village Mušov and above today's beach resort at Pasohlávky. During the reign of the Emperor Marcus Aurelius, the 10th Legion was assigned to control the Germanic tribes who had been defeated in the Marcomannic Wars.[26] In 1927, the archeologist Gnirs, with the support of president Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk, began research on the site, located 80 km from Vindobona and 22 km to the south of Brno. The researchers found remnants of two masonry buildings, a praetorium[27] and a balneum ("bath"), including a hypocaustum. The discovery of bricks with the stamp of the Legio X Gemina and coins from the period of the emperors Antoninus Pius, Marcus Aurelius and Commodus facilitated dating of the locality.
Ancient Moravia: A variety of Germanic and major Slavic tribes crossed through Moravia during the Migration Period before Slavs established themselves in the 6th century AD. At the end of the 8th century, the Moravian Principality came into being in present-day south-eastern Moravia, Záhorie in south-western Slovakia and parts of Lower Austria.
In 833 AD, this became the state of Great Moravia[1] with the conquest of the Principality of Nitra (present-day Slovakia). Their first king was Mojmír I (ruled 830–846). Louis the German invaded Moravia and replaced Mojmír I with his nephew Rastiz who became St. Rastislav.[2] St. Rastislav (846–870) tried to emancipate his land from the Carolingian influence, so he sent envoys to Rome to get missionaries to come. When Rome refused he turned to Constantinople to the Byzantine emperor Michael. The result was the mission of Saints Cyril and Methodius who translated liturgical books into Slavonic, which had lately been elevated by the Pope to the same level as Latin and Greek. Methodius became the first Moravian archbishop, but after his death the German influence again prevailed and the disciples of Methodius were forced to flee. Great Moravia reached its greatest territorial extent in the 890s under Svatopluk I. At this time, the empire encompassed the territory of the present-day Czech Republic and Slovakia, the western part of present Hungary (Pannonia), as well as Lusatia in present-day Germany and Silesia and the upper Vistula basin in southern Poland. After Svatopluk's death in 895, the Bohemian princes defected to become vassals of the East Frankish ruler Arnulf of Carinthia, and the Moravian state ceased to exist after being overrun by invading Magyars in 907.[3]
External links
References
- ↑ Florin Kurta. The history and archaeology of Great Moravia: an introduction. in: "Early Medieval Europe", 2009 volume 17 (3)
- ↑ Reuter, Timothy. (1991). Germany in the Early Middle Ages, London: Longman, page 82
- ↑ Štefan, Ivo (2011). "Great Moravia, Statehood and Archaeology: The "Decline and Fall" of One Early Medieval Polity". In Macháček, Jiří; Ungerman, Šimon. Frühgeschichtliche Zentralorte in Mitteleuropa. Bonn: Verlag Dr. Rudolf Habelt. pp. 333–354. ISBN 978-3-7749-3730-7