Saran
Saran[1]/ (सारण)[2] Saharan (सहारण)/(सहारन)[3] is a Gotra of Jats in Rajasthan,[4] Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana and Madhya Pradesh in India. They were supporters of Bhati Confederacy. [5] [6] [7]
Origin
उदाराम सहारण[8] ने भाट अभिलेखों के आधार पर सहारण जाति का इतिहास निम्नानुसार बताया है: भाटों के अनुसार सहारण गोत्र की उत्पत्ति राजा बलि के पुत्र सारण देव से हुई है। सारण जाट मूल रूप से चन्द्रवंशी राजा ययाति के वंशज है।
सहारण गोत्र की प्रसिद्धि संवत 1122 (सन 1065 ई.) हुई जब राजा सारण द्वारा पुराना नाम वरबुड़ियावास था, सहारनपुर के नाम राज्य की स्थापना वर्ष संवत 1122 (1065 ई.) में हुई। [9]
Jat Gotras Namesake
- Saran = Sarangian = Sarangæ (Pliny.vi.18)[10]
- Saran (Jat clan)= Sarangarh = Saraharagadha (सरहरागढ़) mentioned in Verse-15 of Rajim Stone Inscription of Prithvideva II - Kalachuri Year 896 (=1145 AD).... (V. 15) He made greater (exploits) during the reign of the long Prithvîdêva (II). He captured Saraharagadha (सरहरागढ़), the great fort (preeminent among all) inaccessible fortresses (p.457).....Saraharagadha (सरहरागढ़) was shown by Dr Kielhorn to be the ancient name of Sârangarh (सारनगढ), formerly a feudatory state in Chhattisgarh. (p.453).[11]
Mention by Pliny
Pliny[12] mentions Nations situated around the Hyrcanian Sea.... Beyond the nations already mentioned, are the Chorasmii,13 the Candari,14 the Attasini, the Paricani, the Sarangæ, the Marotiani, the Aorsi,15 the Gaëli, by the Greek writers called Cadusii,16 the Matiani, the city of Heraclea,17 which was founded by Alexander, but was afterwards destroyed, and rebuilt by Antiochus, and by him called Achaïs; the Derbices also,18 through the middle of whose territory the river Oxus19 runs, after rising in Lake Oxus,20
13 An extensive tribe of 'Sogdiana, now represented by the district of Khawarezm, in the desert country of Khiva.
14 A tribe in the north-western part of Sogdiana. They appear to have been situate to the east of the district of Khawarezm. It has been suggested that they derived their name from the Sanscrit Gandharas, a tribe beyond the Indus.
15 The chief seat of the Aorsi, who appear to have been a numerous and powerful people both of Europe and Asia, was in the country between the Tanais, the Euxine, the Caspian, and the Caucasus. It seems doubtful, however, whether it is these people who are alluded to in the present passage.
16 These would almost seem to be a different people from those mentioned in c. 15 of the present Book, as dwelling in Atropatene. The present appears to have been a tribe of Sogdiana.
17 Strabo mentions a town of this name, which he places, together with Apamea, in the direction of Rhagæ. If Pliny has observed anything like order in his recital of nations and places, the Heraclea here mentioned cannot be that spoken of by Strabo, but must have been distant nearly 1000 miles from it.
18 This was a tribe, apparently of Scythian origin, settled in Margiana, on the left bank of the Oxus. Strabo says that they worshipped the earth, and forbore to sacrifice or slay any female; but that they put to death their fellow-creatures as soon as they had passed their seventieth year, it being the privilege of the next of kin to eat the flesh of the deceased person. The aged women, however, they used to strangle, and then consign them to the earth.
19 The modern Jihoun or Amou. It now flows into the Sea of Aral, but the ancients universally speak of it as running into the Caspian; and there are still existing distinct traces of a channel extending in a southwesterly direction from the sea of Aral to the Caspian, by which at least a portion, and probably the whole of the waters of the Oxus found their way. into the Caspian; and not improbably the Sea of Aral itself was connected with the Caspian by this channel.
20 Most probably under this name he means the Sea of Aral.
History
Ram Swarup Joon[13] writes about Saran, Randhawa, Kajla: The Saran gotra is a branch of Bhatti gotra and the Saran Jats are associated with the royal dynasty of Jaisalmer. Their capital was in Bikaner State, which was later occupied by the Rathors. The Sarans live in this area even today.
In the history of this gotra there have been two famous men named Kajal Singh and his son Randhir Singh. Kajal Singh is the forefather of the Kajala gotra of the Jats who mostly live in Bikaner and Haryana.
History of the Jats, End of Page-99
Randhir Singh founded the village of Jhandiala in 1580 in the Punjab and his descendants are called Randhawa. His grandson Targha adopted the Sikh religion and while serving as Jathedar in Patiala misl ruled over Targha Pargana.
Ram Swarup Joon[14] writes about Sheoran, Shivran: According to the bard of this dynasty king Gaj of Ghazni had two sons named Mangal Rao and Masur Rao. Mangal Rao was the ruler of Lahore and Masur Rao of Sialkot. Foreign invaders drove both of them out of their kingdoms. Masur Rao fled away to the deserts of Rajasthan. He had two sons named Abhai Rao and Saran Rao. Descendants of Abhai Rao came to be called Bhurhya Bhatti and those of Saran Rao, Saran. Mangal Rao had six sons, named Mojam Rao, Gulrish, Moolraj, Sheoraj, Kewl Rao and Phul Rao. Descendants of Gulrish came to be called Gloraya or Kiliraya, those of Moolraj, Munda and those Sheoraj, Sheoran. Descendants of Kewal Rao and Phul Rao adopted pottery as their profession and were called Kumhar.
The Sheoran gotra is a big gotra having 52 villages in Luharu 25 in Dadri and 25 big villages in Hissar. People belonging to Kiliraya and Munda gotras are found in Bikaner State.
Sub divisions of Bhati Confederacy
According to H.A. Rose[15] Jat clans derived from Bhatti are: Lahar, Sara, Bharon, Makar, Mond, Kohar, Saharan, Isharwal, Khetalan, Jatai, Khodma, Bloda, Batho and Dhokia.[16]
Villages founded by Saharan clan
- Adsisar (अड़सीसर) - village in Sardarshahar Tehsil of Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Karnaliकरनाली- village in Lunkaransar Tehsil District - Bikaner Raj.
- Ajeetsar - Saran Jats migrated from village Phogabas Bharthari in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district, Rajasthan and founded Ajeetsar village.
- Badasar Churu (बड़ासार) - जैसंग सारण के दूसरी पत्नी का पुत्र बड़ार का पुत्र था देवा। देवा ने देवासर गाँव (देवानिया) बसाया। बड़ार ने बड़ासार बसाया।
- Bakani Sarnon Ki Dhani - village in Gudha Malani Tahsil of Barmer district in Rajasthan.
- Balal - Saran Jats migrated from village Phogabas Bharthari in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district, Rajasthan. Balram Saran founded Balal.
- Bandhnau (बंधनौ) - village in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district in Rajasthan. It is situated in south east direction of Sardarshahar city on Delhi Bikaner Highway
- Bhadang (भाड़ंग) - village in Taranagar tahsil in Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Bilyun - Saran Jats migrated from village Phogabas Bharthari in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district, Rajasthan and founded Bilyu village.
- Buchawas (बुचावास)- village is situated in Taranagar tahsil in Churu district, Rajasthan, India.
- Chiriya चिड़िया - Village In Baytoo Tehsil In Barmer District In Rajasthan.
- Dalman (डालमाण) - village in tehsil Sardarshahar of Churu district in Rajasthan. Dalman village was founded by Dalam Saran (1497 AD)
- Dabri Bari - village in Taranagar tahsil in Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Devasar Churu (देवासर) - जैसंग सारण के दूसरी पत्नी का पुत्र बड़ार का पुत्र था देवा। देवा ने देवासर गाँव (देवानिया) बसाया। बड़ार ने बड़ासार बसाया।
- Gajoosar (गाजूसर) - village in Sardarshahar Tehsil of Churu district in Rajasthan. Saran Jats migrated from village Phogabas Bharthari in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district, Rajasthan and founded Gajoosar village.
- Hardesar (हरदेसर) - village in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Hariyasar Jatan (हरियासर जाटान) - village in Sardarshahar Tehsil of Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Jabrasar (जबरासर) - village in Nohar tahsil of Hanumangarh district in Rajasthan. Jabrasar was founded by Jabra Saran.
- Jaisangsar (जयसंगसर) - village in Sardarshahar Tehsil of Churu district in Rajasthan gets name from its founder Jaisang Saran (जयसंग सारण).[17]
- Jemlani Sarnon Ka Tala (जेमलाणी सारणों का तला) - village in Gudha Malani Tahsil of Barmer district in Rajasthan.
- Jokhasar (जोखासर) - village in Nohar tahsil of Hanumangarh district in Rajasthan. Jokhasar was founded by Jokha Saran.
- Pakka Saharana (पक्का सहारना) - village in tahsil ....in Hanumangarh district in Rajasthan.
- Kanarwas (कानड़वास) - Saran Jats migrated from village Phogabas Bharthari in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district, Rajasthan. Kanhoji Saran founded Kanarwas.
- Dhani Pachera (ढाणी पचेरा) - village in tehsil Sardarshahar of Churu district in Rajasthan. Dhani Pachera was founded by Chaudhari Panchi Ram Saran who came from village Foga.[18]
- Dheerwas Bara (धीरवास बड़ा) - village of Taranagar tahsil in Churu district in Rajasthan. A thikana of Saran clan.
- Kaloosar (कालूसर) - village in Sardarshahar Tehsil of Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Khejara (खेजड़ा)- village in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Jasasar (जसासर) - village in Churu tehsil of Churu district of Rajasthan. Jasasar was founded by Jassa Saharan in Samvat 1421 (1364 AD).[19]
- Malasar Ratangarh (मालासर) - village in Ratangarh tehsil, Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Melusar (मेलूसर) - village in Sardarshahar Tehsil of Churu district in Rajasthan was founded by Melakh Saran.[20]
- Dhani Pachera was founded by Chaudhari Panchi Ram who came from village Foga.[21]
- Kehrani Sarnon Ka Tala (कहरानी सारणों का तला) - village in Gudha Malani Tahsil of Barmer district in Rajasthan.
- Malkisar (मलकीसर) - village is in Lunkaransar tahsil of Bikaner district in Rajasthan. It was founded after Malki, wife of Pula Saran.
- Melusar - was founded by Melakh Saran.
- Phogabas Bharthari (फोगा) - village in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Mitasar - village in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district in Rajasthan
- Nainasar (नैनासर) - Saran Jats migrated from village Phogabas Bharthari in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district, Rajasthan. Nain Saran founded Nainasar.
- Naiyasar (नैयासर) - Saran Jats migrated from village Phogabas Bharthari in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district, Rajasthan. Naiya Saran founded Naiyasar.
- Phogabas Bharthari (फोगा) - is a village in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district in Rajasthan. It was a district of Saran Jat rulers in Jangladesh.
- Pulasar (पूलासर) - village in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district in Rajasthan was founded by its ruler Pula Saran.
- Punras-village in Taranagar tahsil in Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Rajas - Saran Jats migrated from village Phogabas Bharthari in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district, Rajasthan and Raja Ram Saran founded Rajas village.
- Rajasar Beekan (राजासर बीकान) - village in Sardarshahar Tehsil of Churu district in Rajasthan. Founders: Saran. It was earlier known as Laxminarainsar and ruled by Bharatha Saran. [22]
- Saharanpur - Saharan Taka (सहारण टक) was a Nagavanshi Saharan Jat, descendants of Taxaka, who gave name to Saharanpur.[23] सहारनपुर - राजा सारण द्वारा स्थापित किया गया था जिसका पुराना नाम वरबुड़ियावास था। सहारनपुर राज्य की स्थापना वर्ष संवत 1122 (1065 ई.) में हुई। [24]
- Saran district - A district of Bihar state, India.
- Saranon Ki Dhani (सारणों की ढ़ाणी) - village in district Jodhpur
- Saranpura (सारणपुरा) - village in Phalaudi Tahsil of Jodhpur district in Rajasthan.
- Saranwas (सारणवास) - village in Nagaur tehsil & district of Rajasthan.
- Sarayan (सारायण) - village in Taranagar tehsil of Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Sardarshahar (सरदारशहर) - Sardarshahar's old name was Rajiasar founded by Saran Jats. Rathores built a fort here and then first changed it to Sardargarh, later changed to Sardarshahar in name of Kunwar Sardar Singh of Bikaner in 1838.[25]
- Shiv Sarnon Ki Dhani (शिव सारणों की ढाणी) - village in Jodhpur Tahsil of Jodhpur district in Rajasthan.
- Sarniya Khera (सारणियाँ खेड़ा) - village in Amet tahsil of Rajsamand district in Rajasthan.
- Sarnon Ka Tala (सारणों का तला) - named Villages are in Barmer and Gudha Malani tahsils of Barmer district in Rajasthan.
- Sarnon Ki Nari (सारणों की नाड़ी) - village in Chohtan Tahsil of Barmer district in Rajasthan.
- Sarnon Ka Khera (सारणों का खेड़ा) - village in district Bhilwara in Rajasthan.
- Sawai Bari (सवाई) - village in Sardarshahar Tehsil of Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Sirsala Churu (सिरसला) - village in tehsil Churu of Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Thiriyasar (थिरियासर) - village in Sardarshahar Tehsil of Churu district in Rajasthan. Founded by Saran Jats from Phogabas Bharthari in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district, Rajasthan.
- Udasar (उदासर) - village in Nokha tehsil of Bikaner district in Rajasthan
Described by Megasthenes
Saran is one of the Jat clans as described by Megasthenes With 300 cities as the Syrieni (Saharan) along with Derangae (Dengri), Posingae, Buzae (Bajya), Gogiarei (Gugar, Godara), Umbrae (Unvarwal), Nereae (Nehra), Brancosi (Bharangar ), Nobundae (Nawad), Cocondae (Kookana), Nesei (Naij), Pedatrirae (Penda), Solobriasae, Olostrae (Ojlan) Who adjoin the island Patale, from the furthest shore of which to the Caspian gates the distance is said to be 1, 925 miles
In the History of Herodotus
Bhim Singh Dahiya[26] writes that the in the period from ninth century B.C. to the fourth century B.C., roughly the time between the Manda and Van empires and Alexander's invasion, we find numerous tribes of the Jats finding a name in the history of Herodotus and others. Among the tribes of the Medians, we find:
- Busae (the present Bassi)
- the Budii, (the present Bodhi or Budhwar),
- the Phut of the scriptures;
- the Magi (the famous Magian priests).
- The Sagartians may be compared with the Sagarvars;
- the Alarodians may be compared with the Alarod or Aroda of today;
- the Sapiri may be compared with the Sapra of today;
- the Hyrcanias may be compared with the Varkans or Virks of today;
- the Paeonia may be compare with the Paunia/Punia of today;
- the Sarangians may be compare with the Saran of today;
- the Utians with the Utars of today or the Utiya of the Persians.
The ruling people are called Arizanti or Arizatoi. The word Ari is a form of Arya and Zanti/Zatoi are of course the Jats, the Djati of ancient Egypt and the Guti of Sumer and China.
Sanchi inscription
They are mentioned by Cunningham[27] in an inscription at the Buddhist Stupa of Sanchi of the Ashoka period as under:
No. 87. — Aya Rahilasa Sārhineyakasa-Mātu dānam.
- "Gift of Arya Rahila, the mother of Sarhineyaha.
Saran as per Records of Bards
According to the bard of this dynasty king Gaj of Ghazni had two sons named Mangal Rao and Masur Rao. Mangal Rao was the ruler of Lahore and Masur Rao of Sialkot. Foreign invaders drove both of them out of their kingdoms. Masur Rao fled away to the deserts of Rajasthan. He had two sons named Abhai Rao and Saran Rao. Descendants of Abhai Rao came to be called Bhurhya Bhatti and those of Saran Rao, Saran. Mangal Rao had six sons, named Mojam Rao, Gulrish, Moolraj, Sheoraj, Kewl Rao and Phul Rao. Descendants of Gulrish came to be called Gloraya or Kiliraya, those of Moolraj, Munda and those Sheoraj, Sheoran. Descendants of Kewal Rao and Phul Rao adopted pottery as their profession and were called Kumhar. [28]
People belonging to Kiliraya and Munda gotras are found in Bikaner State. [29]
Migration of Saran's
Traditionally Jats consider their origin from the far northwest and claimed ancient Garh Gajni (modern day area between Ghajni, Afghanistan to Rawalpindi, Pakistan) as their original abode.[30] Persian chronicler Firishta strengthened this view and informs us that Jats were originally living near the river of the Koh-i-Jud (Salt Range) in northwest Punjab.[31] The Jats then occupied the Indus valley and settled themselves on both the banks of the Indus River.
By the fourth century region of Multan was under their control.[32] Then they rose to the sovereign power and their ruler Jit Salindra, who promoted the renown of his race, started the Jat colonisation in Punjab and fortified the town Salpur/Sorpur, near Multan.[33]By the end of seventh century, Jats were thickly populated in Deybal region.[34]Their main population was settled in the lower Sindh.The Chachnama stratified these large population of Jats, as 'the western Jats' (Jatan-i-Gharbi) and 'the eastern Jats' (Jatan-i-Sharqi), [35] living on the eastern and western side of the Indus River. The chronicler s further classified them as 'The Jats living on the banks of the rivers (Lab-i-Daryayi) [36] and the Jats living in plain, desert (Jatan-i-Dashti); and 'the rustic Jats' (rusta'i Jat) living in villages.[37]As Jataki, the peculiar dialect of the Jats, also proves that the Jats must have come from the NW Punjab and from other districts (e.g. Multan) dependent upon the great country of the Five rivers.[38]
By the end of fifth and the beginning of the sixth century, Saran's and Jat's southward migration, second in line, took place and they reached Kota in Rajasthan, probably via Bikaner regions. From Kota they migrated further east and established their rule at Malwa under the rule of Salichandra, son of Vira Chandra. Salichandra erected a minster (mindra) on banks of the river Taveli in Malwa.[39] Probably after their defeat by Sultan Mahmud in 1027 AD, and later hard pressed by the Ghaznavi Turkish Commander, the Jats of Sind again migrated to Rajasthan and settled themselves in Bundi regions.[40] The second inscription found at Bundi probably dates from circa samvat 1191 (1135 AD) possibly refers to the Jats as opponents of the Parmara rulers of Rajasthan.[41]
When Muhammad bin Qasim attacked Dahlilah, a fortified town in between Roar and Brahmanabad, most of the inhabitants (the Jats) had abandoned the place and migrated to Rajasthan via desert and took shelter in the country of Siru (modern Sirohi distict) which was then ruled by King Deva Raj, a cousin of Rai Dahir.[42]
However, the third migration took place in early eighth century, Sihag, Godara, Saran,Punia and Jats of lower Sind migrated to Rajasthan, probably via Barmer regions to Bikaner, Ganganagar and Hanumangarh. By the twelfth century, the Jats settled in western Punjab, as the native poet Abul Farj Runi mentions them along with the Afghans.[43] Meanwhile, they also extended their abode in the eastern part of the Punjab (now Haryana to Sirsa and Hisar), as in the end of the twelfth century they resisted Qutb-ud-din Aybak in the region of Hansi.[44]
Saran Rulers in Jangladesh
Earlier they were in Central Asia than they migrated to northern Salt-range Punjab region in India and at the time of Alexander invasion in Punjab in 326 B.C. they fought with Alexander The Great and then Saran along with Sihag,Punia,Godara,Beniwal and Johiya migrated to north Rajasthan region known as Jangladesh and ruled there till 15th century.
Sarans were rulers in Jangladesh. Jangladesh coincided with the princely state of Bikaner in Rajasthan. When Rathores under the leadership of Bika and Kandal were spreading their rule in Jangladesh. At that time Saran Jat were ruling in about 360 villages in Jangledesh. Pula Saran was their king and their capital was at Bhadang town. Bharang (भाड़ंग) is an ancient village in Taranagar tahsil in Churu district in Rajasthan. It is in Raiyatunda Panchayat in east of it. The ancient town was slightly away from the present town some where in between Bhurawas and Sahawa. We find traces of the ancient town in form of ruins and coins etc.
Prior to the rule of Rathores, it was capital of Saran Jats. Khejra, Phog, Buchawas, Suin, Badnu and Sirsala were its districts. Their king's name was Pula Saran and he had 360 villages under him.
As for the Jats prior to coming of Rathors in Rajasthan Nainsi refers to Jat settlements at Bhadang which is identified as the Saran Jatan Ra Des or des belonging to the Saran sept of Jats. [45]
Table of Jat republics in Jangladesh
Dr Karni Singh, a well known political personality and author, records that Jats had established powerful governments in north India. Prior to 1488 Jats had seven Janapadas of Godara, Saran, Sihag, Beniwal, Puniya, Johiya in desert region of Bikaner. Following are the main clans and their heads with capital and number of villages in each territory. [46], [47]
| S.No. | Name of janapada | Name of chieftain | No. of villages | Capital | Names of districts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Punia | Kanha Punia | 300 | Jhansal[48]/Luddi[49] | Bhadra, Ajitpura, Sidhmukh, Rajgarh, Dadrewa, Sankhoo |
| 2. | Beniwal | Raisal Beniwal | 150 | Raisalana | Bhukarkho, Sanduri, Manoharpur, Kooi, Bae |
| 3. | Johiya | Sher Singh Johiya | 600 | Bhurupal | Jaitpur, Kumana, Mahajan, Peepasar, Udasar |
| 4. | Sihag | Chokha Singh Sihag | 150 | Suin/Pallu | Rawatsar, Biramsar, Dandusar, Gandaisi |
| 5. | Saharan | Pula Saran | 300 | Bhadang | Khejra, Phog, Buchawas, Sui, Bandhnau, Sirsala |
| 6. | Godara | Pandu Godara | 700 | Shekhsar | Shekhsar, Pundrasar, Gusainsar Bada, Gharsisar, Garibdesar, Rungaysar, Kalu |
It is thus clear that out of 2670 villages in the Jangladesh, 2200 villages were under the rule of Jats. Each canton bore the name of the community, and was subdivided into districts.
There are evidences of town being in existence in 725 AD. There is temple of Pula Saran. Pandiyas were the priests of Sarans of this area.
Pulasar (पूलासर) is a village in Sardarshahar tahsil in Churu district in Rajasthan. It is situated in southeast direction of Sardarshahar at a distance of few kms. It was founded by its ruler Pula Saran.
Pula Saran's wife was Malki who was abducted by Godara chief Pandu and there was a war with Godara regarding Malki. Sarans had war with Rathores but the Godara Jats had aligned with Rathores due to which Sarans faced a defeat. Godaras were the most powerful among the Jat rulers of Jangladesh. The lack of harmony and coordination among other Jat rulers led to the defeat of Jat states in Jangladesh and established the Rathore Kingdom.
Saran Hinglaj temple - Saran Hinglaj temple is situated near the banks of Hingol River in Samakarata and Khald Pradesh, positioned on the trade routes connecting Baluchistan and Sindh with Gujarat, Jaisalmer, Marwar and Bikaner etc. [50]
Sub sections of Bhatti
According to H.A. Rose[51] Jat clans derived from Bhatti are: Lahar, Sara, Bharon, Makar, Mond, Kohar, Saharan, Isharwal, Khetalan, Jatai, Khodma, Bloda, Batho and Dhokia.[52]
यदुवंश के शाखागोत्र
यदुवंश के शाखागोत्र - : 1. वृष्णि 2. अन्धक 3. हाला 4. शिवस्कन्दे-सौकन्दे 5. डागुर-डीगराणा 6. खिरवार-खरे 7. बलहारा 8. सारन 9. सिनसिनवाल 10. छोंकर 11. सोगरवार 12. हांगा 13. घनिहार 14. भोज ।[53]
ठाकुर देशराज लिखते हैं
ठाकुर देशराज लिखते हैं कि भाट-ग्रन्थों में राव सारन नाम के भाटी और औलाद में हुए लोगों का नाम सारन है। भाट लोग कहते हैं कि सारन ने जाटनी से शादी कर ली थी। इससे उनके वंशज सार कहलाए, यह कथा नितान्त झूठी गढन्त है, जिनका हमने पिछले पृष्ठों में काफी खंडन कर दिया है। सारन वंशीय जाट-क्षत्रिय हैं। सारन व उनके पूर्वज जाट थे। वे उस समय से जाट थे, जिस समय कि लोग यह भी नहीं जानते थे कि राजपूत भी कोई जाति है। जांगल-प्रदेश में उनके अधिकार में 300 से ऊपर नगर और गांव थे। रामरत्न चारण ने उनके अधिकृत गांवों की संख्या 460 बताई है। उनकी राजधानी भाडंग में थी। खेजड़ा, फोगा, बूचावास, सूई, बदनु और सिरसला उनके अधिकृत प्रदेश के प्रसिद्ध नगर थे। राठौरों से उनके जिस राजा का युद्ध हुआ था, उसका नाम पूलाजी था। प्रजा इनकी धन-धान्य से पूरित थी। राज्य में पैदा होने वाली किसी चीज पर टैक्स न था। वहां जो चीजें आती थीं, उन पर भी कोई महसूल न था। कहा जाता है कि जांगल-देश के ब्राह्मण घी, ऊन का व्यापार किया करते थे। राज्य में जितनी भी जातियों के प्रजा-जन थे, सबके साथ समानता का व्यवहार किया जाता था। सारन शांति-प्रिय थे। उनकी प्रवृत्ति थी, ‘स्वंय जियो और दूसरों को जीने दो’। रामरत्न चारण ने अपने लिखे इतिहास में बताया है कि गोदारों जाटों का सरदार पांडु सारणों के अधीश्वर की स्त्री को भगा ले गया, इस कारण जांगल-प्रदेश के सभी जाट-राज्य गोदारों के विरुद्ध हो गए। कहना होगा कि जाटों के लगभग तीन हजार गांवों की सल्तनत को कुल्हाड़ी के
जाट इतिहास:ठाकुर देशराज,पृष्ठान्त-619
बेंट गोदारा पांडु ने नष्ट करा दिया। पांडु यदि राठौरों के हाथ अपनी स्वाधीनता को न बेच देता, तो राठौरों पर इतनी आपत्ति आती कि फिर बेचारे जांगल-प्रदेश की ओर आने की हिम्मत तक न करते। गोदारों की शक्ति अन्य समस्त जाट-राज्यों की शक्ति के बराबर थी। यह नहीं कहा जा सकता कि जांगल-प्रदेश के जाटों को राठौरों ने जीता। जाटों के सर्वनाश का कारण उनकी पारस्पारिक फूट थी। उसी फूट का शिकार सारन जाट हो गए। उनका प्रदेश युद्धों के समय उजाड़ दिया गया और वे पराजित कर दिए गये, किन्तु शांति-प्रिय सारनों ने जो वीरता अपने राज्य की रक्षा के लिए दिखाई थी, वृद्ध सारन जाट उसे बड़े गर्व के साथ अपनी सन्तान को सुनाता है।
भाड़ंग के सारण
भाड़ंग चुरू जिले की तारानगर तहसील में चुरू से लगभग 40 मील उत्तर में बसा था. पृथ्वीराज चौहान के बाद अर्थार्त चौहान शक्ति के पतन के बाद भाड़ंग पर किसी समय जाटों का आधिपत्य स्थापित हो गया था. जो 16 वीं शताब्दी में राठोडों के इस भू-भाग में आने तक बना रहा. पहले यहाँ सोहुआ जाटों का अधिकार था और बाद में सारण जाटों ने छीन लिया. जब 16 वीं शताब्दी के पूर्वार्ध में राठोड इस एरिया में आए, उस समय पूला सारण यहाँ का शासक था और उसके अधीन 360 गाँव थे. इसी ने अपने नाम पर पूलासर (तहसील सरदारशहर) बसाया था जिसे बाद में सारण जाटों के पुरोहित पारीक ब्राह्मणों को दे दिया गया. पूला की पत्नी का नाम मलकी था, जिसको लेकर बाद में गोदारा व सारणों के बीच युद्ध हुआ. [54] मलकी के नाम पर ही बीकानेर जिले की लूणकरणसर तहसील में मलकीसर गाँव बसाया गया था.[55] सारणों में जबरा सारण और जोखा सारण बड़े बहादुर थे. उनकी कई सौ घोड़ों पर जीन पड़ती थी. उन्हीं के नाम पर जबरासर और जोखासर गाँव अब भी आबाद हैं, मन्धरापुरा में मित्रता के बहाने राठोडों द्वारा उन्हें बुलाकर भोज दिया गया और उस स्थान पर बैठाने गए जहाँ पर जमीन में पहले से बारूद दबा रखी थी. उनके बैठ जाने पर बारूद आग लगवा कर उन्हें उड़ा दिया गया.[56][57]
सहारण गोत्र का इतिहास
उदाराम सहारण[58] ने भाट अभिलेखों के आधार पर सहारण जाति का इतिहास निम्नानुसार बताया है:
सहारण गोत्र की प्रसिद्धि संवत 1122 (सन 1065 ई.) हुई जब राजा सारण द्वारा पुराना नाम वरबुड़ियावास था, सहारनपुर के नाम राज्य की स्थापना वर्ष संवत 1122 (1065 ई.) में हुई। [59]
सहारण वंश वृक्ष इस प्रकार बताया है - राजा बलि - राजा सहारण - (पौंडर व) जसरा - पिथरा - मंगलसी -
राजा मंगलसी भाडंग में संवत 1320 चेत बदि 5 (सन 1263) में थे जिनके पुत्र - (जालय व) लूनकरण - सोनगरा- देदा- बीरू- उदा -कालू - देवराज- जास्सा. जास्सा जी ने जास्सासर संवत 1421 (1364 ई.)
जासा के सात पुत्र थे सहसरों, मालक, भेरू, पानी, खानी, गोपी एवं बुद्धा.
बुद्धा जी के पुत्र दलावर -रिड़मल- फ़त्ता- लिखमा- (र्मद व) बीरू - (जसपाल व) दल्लू जी.
दलूजी के 3 पुत्र महरा, मूणा, डूंगर.
डूंगर जी संवत 1845 (सन 1788 ई.) सरदारशहर में बसे. डूंगर जी के पुत्र चेतन जी व जोरू जी, जोरू जी के चार पुत्र सेहो जी, हेमोजी, बीजो जी, टीकू जी.
हेमोजी के पुत्र- पुरुखो जी एवं जेसोजी थे.
पुरुखो जी संवत 1919 (सन 1862 ई.) में मिर्जावाली बस गये, जिनके तीन पुत्र नारायण जी, भादर जी, उदाराम सहारण हैं.
सहारनपुर - इसका नाम पहले बुडिया था. बलि के पुत्र सहारण के नाम पर सहारनपुर हो गया. राजा सारण द्वारा पुराना नाम वरबुड़ियावास था, सहारनपुर के नाम राज्य की स्थापना वर्ष संवत 1122 (1065 ई.) में हुई। [60]
भाडंग - भाडंग नाम का प्रसिद्ध गांव आज भी तारानगर तहसील जिला चुरु में है. संवत 1320 (1263 ई.) में सारण राजा के वंशजों द्वारा भाड़ंग को राजधानी बनाया गया था।[61]
सहारनपुर से राजा मंगलसी सहारण भाडंग पहुंचा. भाडंग उस समय का प्रसिद्ध ठिकाना था जहां जाटों के सहू, सिहाग, जोईया, झोरड़ गोत्र रहते थे. मंगलसी ने उन सबको वहां से निकाल दिया व उस पर संवत 1320 चेत बदि 5 (सन 1263 ई.) में कब्जा कर लिया.
जसासर - यह चुरु तहसील और सरदारशहर तहसील की सीमा के पास चुरु तहसील में आज भी गांव है, जिसको जस्सा सहारण ने संवत 1421 (सन 1364 ई.) में बसाया था.
इस प्रकार सहारण गोत्र का 27 पीढियों का 883 वर्षों का इतिहास उपलब्ध है. पुराने समय में राजस्थान में सहारणों के 360 खेड़े (गांव) की गणना की जाती थी. सहारनपुर के पास 444 गांव सलावा अब तक भौमसिंह पुत्र विजयसिंह राव गांव भड़सिया जिला नागौर की दातारगी में हैं.
पूलासर व राजा पूला सहारण - संवत 1400 (सन 1343 ई.) (तुगलक वंश 1320-1414)
सहारण वंश में संवत 1400 (सन 1343 ई.) में राजा पूला सहारण पूलासर के राजा हुये. पूलासर सरदारशहर से करीब 20 किमी दक्षिण पूर्व में चुरु की तरफ़ एक बड़ा गांव है जहां बोहरा व पांडिया ब्राहमण हैं. पूलासर व राजा पूला के दिल्ली बादशाह की बेगम को जमुना में डूबने से बचाने के बदले दिल्ली का शासन 3-1/2 दिन पूला राजा को देने की कहानी पूलासर के पांडिया ब्राहमण प्रमुख श्री बदरीप्रसाद पांडिया ने लेखक (उदाराम सहारण) को बड़े गर्व के साथ सुनाई. बादशाह ने 2 दिन के पूला के दिल्ली का राज करने के बाद शेष 1 दिन का राज्य चतुराई से बेगम के माध्यम से वापस ले लिया. तब पूला राजा के मंत्री पांडिया ने पूला राजा को कहा कि मुझे क्या दोगे. पूला राजा ने पूलासर ठिकाना इस पर पांडिया ब्राहमणों को दान दे दिया और कहा कि आज के बाद पूलासर में कोई भी सहारण नहीं रहेगा और न ही यहां का पानी पियेगा. इस परम्परा का पालन आज भी जारी है. पूलासर में कोई भी सहारण परिवार नहीं है.
राव भौमसिंह द्वारा भी कहानी तो लगभग यही बताई कि इक्षुराजा के नाम 2-1/2 दिन दिल्ली का शसन किया. 1 दिन वापस दान कर दिया.
पांडिया ब्राहमण आज भी पूलासर व पूला राजा के नाम पर फ़क्र करते हैं व बताते हैं कि पूलासर के पास पूलाना तालाब पर आज भी पूला राजा की समाधी के अवशेष हैं.
राव बीका और राव जोधा की जाटों को समूल नष्ट करने की चाल
राव बीका और राव जोधा ने जाटों को समूल नष्ट करने की चाल चली। उन्होंने राजपूतों को मन्त्र दिया कि हम जाटों से लड़कर नहीं जीत सकते इसलिए धर्मभाई का रिवाज अपनाकर जब विश्वास कायम हो जाये तब सामूहिक भोज के नाम पर बाड़े में इकठ्ठा करो। नीचे बारूद बिछाकर नष्ट करो। इस कुकृत्य से असंख्य जाटों को नष्ट किया गया। [62] बीकानेर रियासत के मुख्य गाँव जहाँ जाटों को जलाया गया -
- जसरासर (चूरू) गाँव के कस्वां जाटों को,
- राजासर बीकान (लक्ष्मीनारायण) के भरता सारण को,
- हरदेसर के सारणों को,
- मालासर (गोगासर के पास) के सारणों को,
- बुकनसर बड़ा डूडीयों को अक्षय तृतीय के दिन,
- सवाई,
- अड़सीसर,
- हरियासर,
- मनहरपुरा,
- सोनडी आदि गाँवों में बारूद से आगजनी की घटनाएँ की। बहुत से गाँवों के पास पुराने थेड़ (खंडहर) पड़े हैं।[63]
सहारण गोत्र का इतिहास
सहरान जाट गौत्र की दो उपशाखाए काजला और रंधावा है|सहारन गौत्र को भाषीय भेद के कारन कही सारण, तो कही सहारण बोला जाता है| उदाराम सहारण[64] ने भाट अभिलेखों के आधार पर सहारण जाति का इतिहास निम्नानुसार बताया है:
सहारण गोत्र की प्रसिद्धि संवत 1122 (सन 1065 ई.) हुई जब राजा सारण द्वारा पुराना नाम वरबुड़ियावास था, सहारनपुर के नाम राज्य की स्थापना वर्ष संवत 1122 (1065 ई.) में हुई। [65]
सहारण वंश वृक्ष इस प्रकार बताया है - राजा बलि - राजा सहारण - (पौंडर व) जसरा - पिथरा - मंगलसी -
राजा मंगलसी भाडंग में संवत 1320 चेत बदि 5 (सन 1263) में थे जिनके पुत्र - (जालय व) लूनकरण - सोनगरा- देदा- बीरू- उदा -कालू - देवराज- जास्सा. जास्सा जी ने जास्सासर संवत 1421 (1364 ई.)
जासा के सात पुत्र थे सहसरों, मालक, भेरू, पानी, खानी, गोपी एवं बुद्धा.
बुद्धा जी के पुत्र दलावर -रिड़मल- फ़त्ता- लिखमा- (र्मद व) बीरू - (जसपाल व) दल्लू जी.
दलूजी के 3 पुत्र महरा, मूणा, डूंगर.
डूंगर जी संवत 1845 (सन 1788 ई.) सरदारशहर में बसे. डूंगर जी के पुत्र चेतन जी व जोरू जी, जोरू जी के चार पुत्र सेहो जी, हेमोजी, बीजो जी, टीकू जी.
हेमोजी के पुत्र- पुरुखो जी एवं जेसोजी थे.
पुरुखो जी संवत 1919 (सन 1862 ई.) में मिर्जावाली बस गये, जिनके तीन पुत्र नारायण जी, भादर जी, उदाराम सहारण हैं.
सहारनपुर - इसका नाम पहले बुडिया था. बलि के पुत्र सहारण के नाम पर सहारनपुर हो गया. राजा सारण द्वारा पुराना नाम वरबुड़ियावास था, सहारनपुर के नाम राज्य की स्थापना वर्ष संवत 1122 (1065 ई.) में हुई। [66]दिल्ली के जाट राजा सलकपाल देव के समय यह बुडिया का राजा था। राजा बलि के ज्येष्ठ पुत्र सहारण देव था। यह वीर पराक्रमी राजा सन 1065 ईस्वी में बुडिया की गद्दी पर बैठा था। यही बुडिया इनके नाम से वर्तमान में सहारनपुर(उत्तरप्रदेश के एक जिला) नाम से प्रसिद्ध है[67]
भाडंग - भाडंग नाम का प्रसिद्ध गांव आज भी तारानगर तहसील जिला चुरु में है. संवत 1320 (1263 ई.) में सारण राजा के वंशजों द्वारा भाड़ंग को राजधानी बनाया गया था।[68]14 सदी के अंत तक जाटों के अलग अलग क्षेत्र पर अलग अलग जाट गोत्रों का शासन था। जिसका आधार गणतांत्रिक प्रणाली थी। उन में से एक मुख्य राज्य था सहारन जाटों का जिसकी राजधानी भाड़ंग थी। इनके अधीन 360 से ज्यादा ग्राम थे। इस साम्राज्य को सारनौटी बोलते थे।
राजा सहारण के बाद जसराज इनके बाद राजा पिथराज हुए यह लोग कई पीढ़ी तक यहाँ के शासक बने रहे जब दिल्ली से जाटों का शासन चला गया और गुलामवंशी मुस्लिम राजा बने तो सामूहिक रूप से यह लोग सहारनपुर से राजा मंगलसी सहारणके नेतृत्व में भाडंग (चुरू जिले में) पहुँचे. भाडंग उस समय का प्रसिद्ध ठिकाना था जहां जाटों के सहू, सिहाग, जोईया, झोरड़ गोत्र रहते थे. मंगलसी ने उन सबको वहां से निकाल दिया व उस पर संवत 1320 चेत बदि 5 (सन 1263 ई.) में कब्जा कर लिया.
जसासर - यह चुरु तहसील और सरदारशहर तहसील की सीमा के पास चुरु तहसील में आज भी गांव है, जिसको जस्सा सहारण ने संवत 1421 (सन 1364 ई.) में बसाया था.
इस प्रकार सहारण गोत्र का 27 पीढियों का 883 वर्षों का इतिहास उपलब्ध है. पुराने समय में राजस्थान में सहारणों के 360 खेड़े (गांव) की गणना की जाती थी. सहारनपुर के पास 444 गांव सलावा अब तक भौमसिंह पुत्र विजयसिंह राव गांव भड़सिया जिला नागौर की दातारगी में हैं.
पूलासर व राजा पूला सहारण - संवत 1400 (सन 1343 ई.) (तुगलक वंश 1320-1414)
सहारण वंश में संवत 1400 (सन 1343 ई.) में राजा पूला सहारण पूलासर के राजा हुये. पूलासर सरदारशहर से करीब 20 किमी दक्षिण पूर्व में चुरु की तरफ़ एक बड़ा गांव है जहां बोहरा व पांडिया ब्राहमण हैं. पूलासर व राजा पूला के दिल्ली बादशाह की बेगम को जमुना में डूबने से बचाने के बदले दिल्ली का शासन 3-1/2 दिन पूला राजा को देने की कहानी पूलासर के पांडिया ब्राहमण प्रमुख श्री बदरीप्रसाद पांडिया ने लेखक (उदाराम सहारण) को बड़े गर्व के साथ सुनाई. बादशाह ने 2 दिन के पूला के दिल्ली का राज करने के बाद शेष 1 दिन का राज्य चतुराई से बेगम के माध्यम से वापस ले लिया. तब पूला राजा के मंत्री पांडिया ने पूला राजा को कहा कि मुझे क्या दोगे. पूला राजा ने पूलासर ठिकाना इस पर पांडिया ब्राहमणों को दान दे दिया और कहा कि आज के बाद पूलासर में कोई भी सहारण नहीं रहेगा और न ही यहां का पानी पियेगा. इस परम्परा का पालन आज भी जारी है. पूलासर में कोई भी सहारण परिवार नहीं है.
राव भौमसिंह द्वारा भी कहानी तो लगभग यही बताई कि इक्षुराजा के नाम 2-1/2 दिन दिल्ली का शसन किया. 1 दिन वापस दान कर दिया.
पांडिया ब्राहमण आज भी पूलासर व पूला राजा के नाम पर फ़क्र करते हैं व बताते हैं कि पूलासर के पास पूलाना तालाब पर आज भी पूला राजा की समाधी के अवशेष हैं.
सारण गोत्र के स्मारक
Saran in Indian epics
We find mention of name Saran in Indian Epics at various places. It is a matter of research if there is any connection of these with the present Saran clan.
Saran in Ramayana
Yuddha Kanda/Sarga 26 in Ramayana mentions about Saran, the spy of Ravana. On hearing the submission of Sarana, Ravana climbs up the roof of his palace and sees the entire army of vanaras from there. Ravana enquires about the various vanara leaders and Sarana shows him Nila, Angada, Nala, Sweta, Kumuda, Rambha, Sarabha, Panasa, Vinata and Krathana the army-generals along with their distinguishing characteristics. Sarana along with Shuka find mention in Ramayana Yuddha Kanda Sarga 26-29.
- तद् वचः पथ्यम् अक्लीबम् सारणेन अभिभाषितम् । निशम्य रावणो राजा प्रत्यभाषत सारणम् ॥६-२६-१॥
- सारण आचक्ष्व मे सर्वम् के प्रधानाः प्लवम् गमाः । सारणो राक्षस इन्द्रस्य वचनम् परिपृच्चतः ॥६-२६-१०॥
Saran in Mahabharata
Adi Parva Mahabharata Book 1 Chapter 211 in Subhadra-harana Parva mentions a grand festival of the Vrishnis and the Andhakas on Raivataka mountain. Sarana along with Gada, Vabhru, Nisatha, Charudeshna etc is mentioned in shloka 10 who accompanied by their wives adorned that mountain-festival. In this festival Subhadra is introduced as uterine sister of Saran.
- अक्रूरः सारणश चैव गथॊ भानुर विडूरदः
- निशठश चारु थेष्णश च पृदुर विपृदुर एव च Mahabharata (I.211.10)
Adi Parva, Mahabharata/Mahabharata Book I Chapter 188 gives list of Kshatriyas who came on Swayamvara of Draupadi. Shloka 16 here mentions Saran:
- संकर्षणॊ वासुदेवॊ रौक्मिणेयश च वीर्यवान
- साम्बश च चारु देष्णश च सारणॊ ऽथ गदस तथा Mahabharata (I.177.16), (1.188),
Sabha Parva, Mahabharata/Book II Chapter 31 gives the Kshatriyas brought tributes on Rajasuya sacrifice of Yudhisthira. This list in shloka 5 mentions about Saran king along with Aniruddha, Vabhru, Gada, Pradyumna, Samba, Charudeshna.
- रामश चैवानिरुथ्धश च बभ्रुश च सह सारणः
- गथ परथ्युम्न साम्बाश च चारु थेष्णश च वीर्यवान Mahabharata (II.31.5)
Vana Parva, Mahabharata/Book III Chapter 267 shloka 52 mentions about Saran as counsellor and officer of Ravana along with Shuka, who came as spies while Rama along with Vanaras were planning to cross the ocean and arrive at Lanka.
- तत्रास्तां रावणामात्यौ राक्षसौ शुकसारणौ
- चारौ वानररूपेण तौ जग्राह विभीषणः Mahabharata (III.267.52)
- चारुथेष्णश च थुर्धर्षस तदैव गथ सारणौ
- अक्रूरश च महाबाहुः किं मां वक्ष्यति सारदे Mahabharata (III.19.20)
In Bhagawata Purana
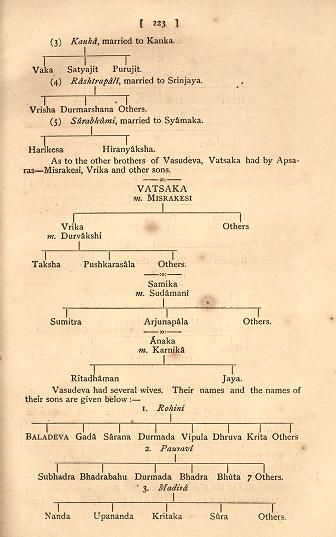
'A study of the Bhagavata Purana; or, Esoteric Hinduism' by Purnendu Narayana Sinha, pp 223 mentions that Vasudeva had several wives. Sarana was brother of Baladeva born from Rohini the wife of Vasudeva.[69]
Saharan In Ramgarh History
Please see page Saharan In Ramgarh History
Distribution in Rajasthan
Locations in Jaipur city
Adarsh Nagar, Ambabari, Bagruwalon ka Rasta, Bapu Nagar, Bhagwati Nagar, C-Scheme, Gandhi Nagar, Hanuman Nagar, Kailashpuri, Khatipura, Mansarowar Colony, Murlipura Scheme,
Villages in Jaipur district
Akoda, Khandel Jaipur (1), Khuriyal, Lakholai Phagi (6), Mukundpura Dadawata (2), Pratappura Phagi (2), Sunadiya (1), Tootoli (7), Mamana Dudu, Mangalwara, Meerapura,
Villages in Ajmer district
Kotri Ajmer, Ralawatan (3), Sursura (1),
Villages in Alwar district
Sheetal Ka Bas,
Villages in Dausa district
Villages in Jodhpur district
Aau, Agolai, Amla, Artiya Kalan, Bagoriya, Balesar Durgawatan, Bambore Darjiyan, Bhavi, Birawas (7), Bisalpur, Boyal, Chamu, Daikara, Hiradesar, Jaleli, Janadesar, Jati Bhandu, Jhanwar, Jodhpur, Keru, Khariya Khangar, Khinchan, Kuri, Lawera Kalan (10), Mathaniya, Matora, Nandara Kalan, Nandiya Khurd, Ostaran, Panchla Khurd, Phalaudi, Raikoriya, Raimalwara, Ratkudia, Sadri, Salwa Kalla, Samrau, Saranon Ki Dhani (Madlakhurd), Saranpura, Shiv Sarnon Ki Dhani,
Villages in Nagaur district
Anwaliyasar, Arwar, Bagrasar, Bajoli, Bakaliya, Barani Nagaur, Barnel (Parbatsar), Basni Khaleel Berathal Kalan, Bhaiya Khurd, Chheela Nagaur, Chittani, Degana Ganw, Dadhwara, Deshwal, Dhatiyad, Dhundhiyari, Gachhipura, Gigaliya, Gotan, Gunsali, Jhadisara, Kameriya, Kantiya, Kheri Leela (65), Khundala, Lambi Deri, Maharana, Mandeli, Meharana, Nagri, Narwa Kalan, Peempasar, Raidhanu, Rasal, Ridmalas, Rol, Saranwas, Sarunda, Satheran, Udaipura,
Villages in Barmer district
Aadel, Adarsh Goliya, Adarsh Katarla, Akarli Dhansingh, Amarji Ki Dhani, Aasuon Ki Dhani, Bakani Sarnon Ki Dhani, Balewa, Balotra, Banta (बांटा), Barmer, Basra-Ramsar, Bataru , Baytu, Bayatu Panji, Beriwala Tala (बेरीवाला तला), Bhachbhar, Bhadrai, Bheemra, Boonth Jet, Chabawas, Chandesara, Chari Barmer, Chawa, Chhitar Ka Par, Chiriya, Chokhala, Dharasar, Doodhu, Garal (15), Goliya Jetmal, Jaydoo, Jemlani Sarnon Ka Tala, Jhakh, Jhingi Nadi (150), Kalyanpur, Kanasar (t. Sheo), Kanasar (t. Sheo), Kanor, Kasoombala Bhatiyan, Kashmir (कश्मीर), Kehrani Sarnon Ka Tala, Kekad, Kharapar, Kharin, Korna, Kosariya, Koshlu, Kothala, Kotra Barmer, Madhasar, Malpur, Mandrooponiyon Ki Dhani, Mokhab Khurd, Naukh (10), Naya Bhuratia (Kawas), Nokhra (15), Pareu, Pabubera[70], Pooniyon Ka Tala, Purawa, Rangwali, Rateu, Ratasar, Rawatsar, Sahar, Sanawara Kalan, Sanwlor, Sarnon Ka Tala (t.Chohtan), Sarnon Ka Tala (t.Gudha Malani), Sarnon Ka Tala (t.Gudha Malani), Sarnon Ki Beri (t.Pachpadra), Sarnon Ki Nari (t.Chohtan), Sarnu, Savau, Sawau Moolraj Baytu, Sawau Padamsingh, Sindhari, Sobhala Jetmalan (50), Swamiyon ki Beri, Taratara Math, Umarlai Khalsa, Mewa Nagar
Villages in Jaisalmer district
Villages in Pali district
Bera Ghenadi (Dadia), Chandawal Nagar, Dhundhla (Sojat), Mandiyan, Ramawas Khurd, Sarangwas (Sojat), Sojat Road,
Villages in Jalor district
Chitalwana, Dabli, Gundau, Khara, Lalji Ki Dungari, Mirpur Kheda,
Villages in Sikar district
Chuwas, Hudera, Mirjwas, Punyana (5), Ghirania Bara
Villages in Churu district
There are 90 villages of Saharan Jats around Churu. Villages inhabited by Saharans are: Abasar, Ajeetsar, Alsar, Amarsar Sujangarh, Bairasar Manjhla, Balal, Balrasar (6), Bandhnau, Bandwa, Basnau , Bhalau Teeba, Bhagela, Bhanin, Bhanipura Churu, Binadesar (4), Baniyala Baen, Beenasar, Bharang, Bheroonsar, Bhojrasar, Bhuwari, Bidasar, Bilyun, Boghera, Buchawas, Bukansar Bara, Chadsar, Chhabri Khari, Chhapar Churu (30), Chimanpura, Dabri Badi, Dalman (150), Devipura Rajgarh, Devasar Churu, Dhana, Dhani Asha, Dhani Doodgir, Dhani Panchera, Dheerasar Charnan, Dheerwas Bara, Dheerwas Chhota, Dhingi, Dhigharla, Dhanauti Bari, Gagore, Godas, Gajoowas, Gajsar, Gajusar, Gidgichia, Golsar, Gothyan Bari, Gusainsar, Hariyasar Jatan, Harpalu, Heera Ka Bas, Jaisangsar, Jaitasar, Jhotaran, Jigsana Tal, Jorji Ka Bas, Jyak, Kadia, Kailas, Kaloosar, Kanarwas, Kandhalsar, Karansar, Karejra, Dhana Kaswan, Katar Bari, Khasoli, Khejaran, Khudi Khari (70), Kohina, Lachhadsar, Lalgarh, Lohsana Bara, Malsar, Malaksar, Manpura Rajgarh, Melusar, Naiyasar, Nainasar, Nangal Bari, Nethwa, Pahadsar, Parewara, Phogabas Bharthari, Pulasar, Pichakaraien taal, Paharsar (70), Poonusar (2), Punras, Rajas, Ratanpura, Ratnadesar (15), Ragha Choti, Ragha Bari, Raiyatunda, Rajpura, Ramsisar, Ratanpura, Rewasi, Sahawa, Sangasar, Sardarshahar, Sarsar, Satyun, Seowa, Shimla Sardarshahar, Simsiya, Sirsala, Sujangarh (36), Suratpura, Thiriyasar, Tidiyasar, Togawas, Udasar, Udasar Bidawatan, Udsar, Udsar Lodera, Udwala, Dhani kulriyan, Devipura, Nangal Bari, Hameerwas,
Villages in Bikaner district
Arjunsar Station, Bajju, Bandhra, Berasar, Bhamatsar, Beegawas Ramsara, Bikaner, Garhwala, Kisnasar, Kolayat, Nathusar, Lalam Desar Bara, Rajpura Huddan, Ramnagar, Kuntasar (2), Takhatpura, Udasar,
Villages in Hanumangarh district
22 ndr, Ayalki, Aradki, Amarpura Rathan, Bashir, Bhaguwala, Bhagwan, Bhairusari, Bharwana, Bhojasar, Biran Hanumangarh, Bolanwali, Chahuwali (चहुवाली), Chaiya, Chanan, Chhani Badi, Chhapanwali, Chindalia, Dabli Khurd, Daulatpura Tibbi, Deeplana, Deidas, Dhaban, Dhadheta, Dhandhela, Dingarh, Ghotda, Gogameri, Goluwala, Hanumangarh, Jasana, Jorawarpura Hanumangarh, Kaluana, Khachwana, Kharachak, Kharakhera, Khiyania, Khothanwali, Khinania, Kishanpura Utradha, Kular, Kulchander , Lakhe Wali Dhab, Makkasar, Malkhera, Maliya Nohar, Manak Thedi, Manuka, Morjand Khari, Matorian Wali Dhani, Nagrana, Nathor, Nathwana, Nukera, Nyaulkhi, Pacca Saharana (पक्का सहारणा), Pakki Dabli, Panditanwali, Peerkamadia, Phephana, Pilibanga, Piperan, Rajpuria, Ramgarh Ujjalwas, Ramgarh, Ratanpura Hanumangarh, Ratanpura Nohar, Ratna Desar, Rohidawali, Saharani, Saliwala, Silwala Kalan, Silwala Khurd, Sangaria, Sri Dungarsingpura, Teja Khera, Thalarka, Tidiyasar, Toparia, Topariya Barani,
Villages in Sri Ganganagar district
17 LNP, 10 spd, 46 RBA Padampur, Amarpura Jatan, Bakhtana 13Q, Bhompura, Binjhbaila, Chak 1F Chhoti, Chak CH.RUPA RAM WALA , Jyodi 15/16 LLG, Chak Manphool Wala, Chak-4z ii, Dhingawali Jatan, Dungar Singh Pura, Ganeshgarh, Gharsana, Kalwasia, KSD Dhani, Ladhuwala, Lalgarh Jatan, Likhmewala, Madhera, Mammad, Mahiyanwali, Purani Abadi, Rawla, Sadhuwali, Sadulshahar, Sardarpura Jiwan, Tatarsar,
Villages in Jhunjhunu district
Bhainsawat Kalan, Birol, Khedar Ki Dhani,
Villages in Tonk district
Bagpura (1), Bhairupura (5), Kachaulya (1), Kala ki Dhani (1), Naya Dhila (1), Pandreda (1),
Villages in Bhilwara district
Sarnon Ka Khera, Saran Ka Khera (t.Mandalgarh),
Villages in Sirohi district
Saran Ka Khera (t. Reodar),
Distribution in Haryana
Villages in Bhiwani district
Villages in Kaithal district
Dubal (दूबल), Kharak, Kole-Khan (कौलेखाँ),
Villages in Jind district
Villages in Hisar district
There are 24 villages of Saran Jats in Hisar district. Villges are:
Badchhapar (बड़छपर),
Bagla,
Bandaheri,
Chaudhriwas,
Hasangarh (हसनगढ़),
Julana (जुलाना),
Kaimri,
Kharia Hisar,
Khedar,
Kherti (खेरटी),
Kuthara (कुठारा),
Ladwi,
Muklan (मुकलान),
Parbhuwala,
Riyasar (रियासर),
Sarsana (सरसना),
Virwal (विरवाल),
Yajara (याजरा),
Villages in Sirsa district
Ali Mohammad, Asa Khera (आसा खेडा), Barasari (बरासरी), Bhadra Sirsa (भादड़ा), Chautala, Dhingtania (धिंगतानिया), Farmana Khas (Meham), Jhittikhera, Kaluana, Kalwana, Lakhuana, Jasania (जसनिया), Nuhiyan Wali, Shakar Mandori (शकर मंदोरी ), Shergarh(शेरगढ़ में सिख सरन है)
Villages in Fatehabad district
Villages in Rohtak district
Farsana (फरसाना) , Farmana Khas, Madina (मदीना), Bhaini Chandrapal (भैनी चंद्रपाल) , Singhpur (सिंहपुर) , Nidaana (निदाना) , Vailwa (वैलवा) , Saiman (सैमाण) ,
Villages in Kurukshetra district
Villages in Yamunanagar district
Distribution in Gujarat
Villages in Banas Kantha district
Distribution in Punjab
Bhagsar, Kular, Panchkosi, Julani,
Villages in Fazilka district
Daulatpura Abohar, Lakhe Wali Dhab, Ramkot, Shehtirwala,
Villages in Firozpur district
Villages in Ludhiana district
- Saharan Majra is village in Payal Tahsil in Ludhiana district, Punjab.
Villages in Hoshiarpur district
Villages in Bathinda district
Jodhpur Bagga Singh Alias Phalran
Distribution in Madhya Pradesh
Saharan gotra Jats are found in MP in many districts. They are at Atarsama Harda, Bhopal, Harda, Intkheri (Raisen),
Villages in Mandsaur district
Molyakheri, Rajnagar (Sitamau), Ralayta (Haidra Mata),
Villages in Nimach district
Fatehnagar (3), Jawad (1), Kundala (1), Khadawda (4), Malaheda (1),
Villages in Ratlam district
Villages in Ratlam district with population of this gotra are:
Badauda 12, Bangrod 1, Banjali 2, Bardiya goyal 2, Bhatkheda 1, Bilpank 2, Damottar 2, Dantodiya 2, Dhamottar 2, Dhaunswas 9, Dheekwa 13, Ghatwas 1, Jawra 1, Jharsandala 1, Kalkheda 19, Kalori 2, Kalori khurd 1, Kotdi 1, Narayangarh sailana 1, Negarda 10, Panched 4, Panchewa 12, Piploda 28, Raoti 1, Ratlam 3,, Rupa kheda 22, Sikhedi 3, Surana 7,
Villages in Harda district
Abgaon Kalan, Atarsama, Baidi, Bhadugaon, Bichhola, Devtalab, Goyat Harda, Harda, Kartana, Khardana, Kolipura, Kunjargaon, Kusia, Nimakhedi, Pidgaon, Rijgaon,
Villages in Sehore district
Gopalpur Sehore, Jamonia Kalan(Pandagaon), Muhai,
Villages in Dewas district
Barchhakhurd, Digod Dewas, Jhirnya, Tipras, Gola Guthan, Kothmir, Mehandul, Melpipalya, Piplani, Hatpipalya,
Villages in Khargone district
Villages in Dhar district
Badnawar, Dhamana Dhar, Dhamnod, Kalola, Kanvan Dhar, Paduni Khurd, Padunya, Sundrel,
Villages in Barwani district
Villages in Ujjain district
Barkheda Tarana, Karondiya, Khandoda,
Villages in Indore district
Distribution in Uttar Pradesh
सारण (सहारण ) गोत्र के जाट उत्तर प्रदेश में 20 गाँव निवास करते है । जो की मेरठ ,बिजनोर ,मुज्ज़फर नगर ,शामली,बिजनोर ,गाज़ियाबाद बुलंदशहर ,हापुड़ ,सहारनपुर,बरेली जिले में है । सारण इतिहास के अनुसार सारण जाट उत्तर प्रदेश में राजस्थान से जाकर बसे थे । सहारण खाप के गाँव निम्न है नगला शेरपुर, सुल्तानपुर, अलीपुर, अटलपुर, भदौरा, चिन्दोदी, रामपुर, सिसोला, नावडिया, राजपुर छाजपुर, चंदौड़ी, खेडा गदई, मुबारकपुर सहारण मीरपुर ,पीपली ,अमनुल्लापुर ,समसपुर ,लूखरदा ,सांपला,बीनपुर बीबीनगर,भैसखुर| Information add by- Manvendra Singh Tomar |
| सहारण/सारण खाप उत्तर प्रदेश के गाँवों की सूची |
|---|
| जिला | गाँव का नाम |
|---|---|
| मेरठ | अमनुल्लापुर |
| मेरठ | मीरपुर |
| मेरठ | पीपला |
| मेरठ | अट्टा चिंदोती |
| मेरठ | अटलपुर |
| मेरठ | आत्मदपुर अलीपुर |
| मेरठ | भदौड़ा |
| मेरठ | समसपुर |
| मेरठ | मीरपुर |
| मेरठ | रामपुर |
| मेरठ | सिसोला |
| मेरठ | मुज़क्कीपुर |
| हापुड़ | लूखरडा |
| सहारनपुर | बीनपुर |
| शामली | सांपला |
| शामली | खेड़ी गदाई |
| मुज़फ्फरनगर | राजपुर छाजपुर |
| मुज़फ्फरनगर | पिंडोरा |
| मुज़फ्फरनगर | चंदौड़ी |
| मुज़फ्फरनगर | ऊन |
| गाज़ियाबाद | नगला शेरपुर |
| गाज़ियाबाद | सुल्तानपुर |
| रामपुर | नवाडिया |
| बिजनोर | मुबारकपुर |
| बुलंदशहर | बीबीनगर |
| बुलंदशहर | भैंसौरा |
| बरेली | |
| मुरादाबाद |
Villages in Meerut district
Aatta chindodi / Chindhori, Atalpur, Alipur, Amanullapur, Bhadaura, Meerpur, Muzakkipur, Meerpur Peepali, Samaspur, Rampur, Rampur Moti, Sisola,
Village in Ghaziabad district
Villages in Rampur district
Villages in Mujaffarnagar And Shamali district
Chandaudi, Khera Gadai, Oon (ऊन), Pandaura, Rajpur Chajpur, []Samapla]]
Villages in Saharanpur district
Villages in Hapur district
Villages in Bulandshahar district
Villages in Bijnor district
Mubarakpur Saharan (t.Najibabad),
Distribution in Pakistan
Hindu
Saran Hindu Jats are residing in Umarkot, Tharparkar, Mirpurkhas and Sanghar districts of Sindh Province,Pakistan and Punjab (Pakistan).
Muslim
The Saran were another Mulla Jat clan found mainly in Hissar and Sirsa. Like other Mulla Jat clans, they emigrated to Punjab (Pakistan) after partition.
Gallery of Saharans
Pula Saran (1487), Bharang, Churu
Bhartha Saran (1614)
Pankaj Saran, Indian Foreign Service
Chetan Ram Saran (left)
Om Prakash Saran, Piploda Ratlam
Sardara Ram Saran from Chotala, associated with Gramothan Vidyapith Sangaria
Sepoy Urja Ram Saran (1940-1971)
Shahid Babu Ram Saran
Notable persons
- Saran Rao was son of Masur Rao, who was son of Raja Bhatti, grandson of Raja Baland and great grandson of Salivahana (S.72 = AD 16).[71]
- Suraj Saharan founder of Delhivery
- Pula Saran (1487 AD) - Jat ruler of Jangladesh, Founder of Pulasar.
- Bhartha Saran (1614) was a Jat ruler of Jangladesh region in Rajasthan prior to formation of Bikaner princely state of Rathores.
- Jokha Saran - Jat warrior, Founder of Jokhasar
- Jabra Saran - Jat warrior, Founder of Jabrasar
- Melakh Saran- Jat warrior, Founder of Melusar
- Daulatram Saharan - Great politician & Founder of Raj. Kisan Union in 1974
- Randhir Singh Saran - founded the village of Jhandiala in 1580 in Punjab, his descendants are called Randhawa, p.100
- Mahasati Dadi Khinwani (1588) - Khinwani, seven year girl of Saran clan of Shimla Sardarshahar village in Churu district of Rajasthan. She was engaged to Jaita Ram Sihag who died in war and Khinwani became sati in year 1588 AD. There is a grand temple built on this samadhi.
- Choudhary Ruparam Saran चौधरी रूपाराम सारण- बीकानेर जिले के लूणकरणसर तहसील में करनाली गांव के रहने वाले जनसेवी एवं समाज सेवी जिन्होंने आसपास के क्षेत्र में समाज सेवा का काम किया।
- चौधरी दुदाराम सारण: (1929-2019) बन्धनाऊ , सरदार शहर(चुरू), जीवनपर्यंत गौसेवा का काम किए तथा सामाजिक कुरीतियों के विरूद्ध कई आन्दोलन किए।
- Subedar Shivji Ram Saharan - freedom fighter from village Dalman in Sardarshahr tehsil of Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Ram Krishan Saran - National Karate Player from village Udwala in Bidasar tehsil of Churu district in Rajasthan.
- Bahadur Singh Saran (चौधरी बहादुरसिंह सारण), from Phephana (फेफाना), Hanumangarh, was a Social worker in Hanumangarh, Rajasthan. [72]
- Chunna Lal Saran (born:1900) (चुन्ना लाल सारण), from Makkasar (मक्कासर), Hanumangarh, was a social worker in Nagaur, Rajasthan.[73]
- Kana Ram Saran (चौधरी कानाराम सारण), from Jhadisara (झाड़ीसरा), Nagaur, was a social worker in Nagaur, Rajasthan.[74]
- खिंया राम सारण, वाडाणी - मारवाड़ जाट कृषक सुधार सभा की प्रबंधकारिणी और कार्यकारिणी में रहकर आप ने जाट जाति की सेवा करके अपने को कृतार्थ किया है। [75]
- Ayush Saran is a paira kamishand officer from Barmer Raju Ram saran (Father) and Hiron Devi (Mother)
- भूला राम सारण, दुगस्ताऊ - मारवाड़ जाट कृषक सुधार सभा की प्रबंधकारिणी और कार्यकारिणी में रहकर आप ने जाट जाति की सेवा करके अपने को कृतार्थ किया है। [76]
- सुल्तान सारण, रतकुड़िया - मारवाड़ जाट कृषक सुधार सभा की प्रबंधकारिणी और कार्यकारिणी में रहकर आप ने जाट जाति की सेवा करके अपने को कृतार्थ किया है। [77]
- Surja Ram Saran - Freedom fighter from Rajasthan
- Khayali Saharan - Laughter king (Acted in 'Sing is King')
- Rajinder Kumar Saharan - Wrestler winner of Gold Medal in 55kg, Greco-Roman style in Commonwealth Games Delhi 2010.
- Pankaj Saran - Indian Foreign Service
- Om Prakash Saharan - RAS, Rajasthan
- T. C. Saharan - RAS ,Rajasthan
- Tara Chand Saharan - Ex IPS, Rajasthan
- Bala Ram Saran - Martyr of 1965 Indo-Pak War
- Lala Ram Saran - Martyr
- Chetan Ram Saran - Ashok Chakra Vijeta
- Jagram Puri (Saran) - Taratara Math (Barmer)
- Surender Singh Saharan - Criminal Lawyer Delhi High Court
- Ram Nath Saharan - RPS ,Rajasthan
- Lt. Col. Ganga Ram Saran - Anandnagar, Jaipur.
- Ugrasen Saharan - Social worker from village Nathusar district Bikaner Rajasthan
- D C Saran - Author & Social worker.
- Sant Captain Lalchand - Saran Gotra from Churu district, Rajasthan
- Jawra Ram Chaudhary (Saran) - RAS
- Akali Phoola Singh - Saharan Jat, Senapatin of Maharaja Ranjit Singh of Punjab and jatthedar of Akal Takht
- Jawahar Chaudhari Saran - RAS (2005) from village Rawatsar Barmer (Barmer), DOB:1-1-1974
- Sqn.Ldr.Veena Saharan - First woman co-pilot to fly IL-76, declared Best Lady pilot Officer
- R.S.Saran( Farmana-Rohatak) - Ex Chief Controller of Shipping, Govt. of India
- Chaina Ram Saharan - RAS, Home District : Barmer
- Har Lal Saran - RAS, UDAIPURWATI, 9414308340
- Joga Ram Saran - Journalist Barmer. Author of book 'Barmer Ke Jat Gaurav' Released on 12 July 2009.
- N K Saran- Officer in Police Force.
- Ajay Kumar Saran - Dy. Commandant BSF, Date of Birth : 23-August-1978, NEAR KISAN HOSTEL, Sardarshahr, Churu - 331403, Present Address : DY COMMANDANT/ MT SHQ BSF BIKANER,SAGAR RD,BIKANER (RAJ), Resident Phone Number : 01564-220397, Mobile Number : 9461134035, Email Address : ajaysaran021@gmail.com
- B. R. Saharan - Prof.(Retd.),Zoology, Date of Birth : 15-January-1948. Vill.- Dhani Panchera, Teh.- Sardarshahar, Distt.- Churu, Present Address : 21/81,MLA Quarters,Kaveri Path, Mansarowar, Jaipur- 302020, Resident Phone Number : 0141-2392211, Mobile Number : 9829057622
- Col. Hari Singh Saharan - Prsident, All India Saharan Pariwar Samaj Sewa Samiti. Colonel, Date of Birth : 11-July-1953, Present Address : 158, Mahadev Nagar, Near Vaishali Nagar, Gandhi Path, Jaipur - 302021, Resident Phone Number : 0141-4001550, Mobile Number : 9660903606, Email Address : saharanhari@yahoo.co.in
- Ram Lal Saran - DGM (Fin.) Airport Authority of India, Date of Birth : 1-January-1960, VILL.- Kishanasar], PO- Garbadesar TEH.-Lunkaransar,Distt.- Bikaner, Present Address : 10/878, MALVIYA NAGAR, JAIPUR, Resident Phone Number : 0141-2722102, Mobile Number : 8107785762, Email Address : rlsaran@aai.aero
- H. R. Saharan - Chief Manager Bank Of India (Retd.), VPO - Bakhtana 13Q, Teh.& Distt. - Sri Ganganagar, Rajasthan, Present Address : 40/91, Mansarovar, Jaipur, Phone: 0141-2390722, Mobile : 9414602948, Email Address : hrsaharan@yahoo.com
- Mani Ram Saran - Chief Engineer (Retd.) Ground Water Deptt., Date of Birth : 1-August-1948, VPO- Khejaran, teh.- Sardarshahar, distt. - Churu, Raj., Present Address : A-83 , Urmila Marg ,Hanuman Nagar, Jaipur, Phone Number : 0141-2352419, Mob: 9461481711
- Dayaram Saharan Ramgarh - प्रदेश उपाध्यक्ष, प. चि. क. संघ, राजस्थान L.S.A. Veterinary Hospital,Phephana Date of Birth : 4-5-1977, VPO- Ramgarh, teh.- Nohar, distt. - Hanumangarh, Raj., Present Address :Ward no.1,Balaji Nagar,Nohar, Mob: 9829635298
- Nimba Ram Saran - RPS from village Sawau Padamsingh (Barmer),
- Mangi Lal Saran - Commandant BSF, from village Kharin (Barmer),
- Late Shri Jotram Saharan Ramgarh Nohar Hanumangarh
- Daulat Ram Saran Dalman: Sanrakshak Jat Kirti Sansthan Churu
- Mahander Singh Saharan - Maha Sachiv M/S All India Saharan Pariwar Samaj Sewa Samiti, Mob: 09810418495. Prop. Shri Babosa Cargo Relocation Gurgaon. Vil. Chubkiyagarh, Rajgarh Churu, Rajasthan.
- Santosh Kumar Saran - MLA Sadulshar Vidhansabha
- Banwari Lal Saharan - Social worker, From Ellenabad,Haryana,
- Surender Singh Saharan - Prop M/S Sunrise Road Carrier Kapashera New Delhi, From village Bagla, dist Hissar, Haryana, Mob: 09811627474, 09311221007
- Amir Singh Saharan- Village Bhadashapur, Farmana, Haryana, Bhim Awarad (Haryana) - 2000, Bharat Arjun Awarad 2002, Baliwal top ten palayers
- Vijandar Singh Saharan - Farmana State Gernal Secretary Haryana Pharmacist Assocaition, All India vice President Fedration of Indian Pharmacist Orgenisation, Haryana Govt Awarad Bety Bachao, Mob: 09255121576
- Jitandar Saharan - Farmana Maham Social workar and politician, INLDm Mob: 0981289400
- Dr Dharamvir Singh Saharan - retdMD AIIMS Delhi, retd Helth Director of Haryana Govt. Mob:9810009877, lives in Gurgaon
- Dharamvir Dingh Saharan - Congress leader, Vice Chairman Jila Parisad Kaithal, Haryana, Mob:9891758023
- Mahavir Singh Saharan - Xen DHVN Gurgaon.
- Bhoop Singh Saharan - Birla Group, Delhi. 29 Prthvi Raj Road, India Gate New Delhi
- Jayparkash Saharan - urf JP ex. Minister Govt of India and Haryana Govt. Congress leader in Haryana.
- Dr Arvind Kumar Saharan - Saharan Nursing Home Rurkee, Dist Haridwar, Uttarakhand, Mob: 09760327742
- Krishan Kumar Saharan - S/O Daulatram Saharan Ex. Minister & politician from Rajasthan
- Puspendar Saharan - Advoct Muzaffarnagar, UP, Mob: 09045538808, Member of All India Saharan Pariwar Samaj Sewa Samiti
- Dharveer Saharan - Jat Maha Sabha Pardhan Meerut, UP, Phone: 0121- 2682336
- Depandar Saharan - Political leader BSP, Meerut, UP
- Sayodhan Singh Saharan - Garam Pradhan Chindori, Meerut, UP
- Mukesh Saharan - Chindori, Meerut, UP. Member of All India Saharan Pariwar Samaj Sewa Samiti, Ph: 0121-2886238, Mob:09411643518
- Dr Surendar Pal Singh Saharan - s/o Sh Motiram Saharan, Shri Gaganagar
- Dr Birajmohan Saharan - S/O sh chetan ram saharan ghaneshgarh shri gaganagar
- Ramnarayan Saharan - Industrial president bhiwadi mfg association
- Ridhi Nath Ji Saran - From Balak village in Hisar district. इनके मामाजी का नाम भागमल चौधरी था। रिधिनाथ जी ने इलाहबाद त्रिवेणी पर कठोर तप किया था। इन्होने कुम्भ मेले पर 360 चेलों को मूंडा था। इनके शिष्य जगजीवननाथ गिरी ने विक्रम संवत 1415 में पण्डरेउ मठ की नींव रखी थी। इस मठ की कीर्ति उस समय श्रीपंचजूना जगजीवननाथ गिरी अखाडा के रूप में सबसे ऊपर थी।
- संत कैप्टन लालचन्द - जिला चुरू के रहने वाले सहारण गोत्री जाट जिन्होंने एक नया अध्यात्मक विचार पैदा किया।
- Dhiru Ram Saharan - Samaj Sewa Samiti memorial trust Shiv Shakti reped x fors rishi nagar hissar haryana
- Dr Surender Saharan
- Anamika Saran - RJS
- Gauri Shankar Saran - Son of Shrawan Kumar Saran, DOB:7-5-1994, Got 88.17% marks in tenth, 95.08% (year 2010-11) in Senior Secondary Science Group with 9th rank, Selected in IIT Bombay. His great grandfather was Shyoji Ram Saran a leading reformer of the area who participated in 1934 Jat Prajapati Mahayagya in Sikar along many villagers. [78]
- Sepoy Urja Ram Saran (1940-1971) from village Samrau in Osian tahsil of Jodhpur district in Rajasthan became martyr during Indo-Pak War 1971.
- Harpal Singh Saharan-[ Chief Engineer in Merchant Neavy Village Julani Distt Jind Haryana]
- Jagdish Saharan - RAS (2012), from Baytu (Baytu, Barmer) [79]
- Bhanwar Lal Saharan - RAS (2012), from Baytu (Baytu, Barmer) [80]
- Anju Chaudhari (Saharan) - She got elected as Member of Vest-Agder County Council in Norway. Currently she is Member of Transport, Area and Environment Committee in Vest-Agder County.
- Lans Hawaldar Babu Ram Jat (Saran) (15.12.1966-18.11.2013) - Village Chamu, Shergarh, Jodhpur, 2 Jat Regiment became martyr of militancy in Rajauri Sector of Jammu and Kashmir on 18 November 2003 during 'Operation Prakram'.
- Jawahar Chaudhari Saran - RAS (2006) , DOB:1-1-1974, CEO zila parishad, Jalore, From : village Rawatsar Barmer (Barmer), M: 9829441699
- Bharat Saran is Dr from Barmer who provides coaching through an Institute by the name '50-Villagers' to the needy students to get admission in NEET and All India Institute of Medical Sciences.
- Chain Singh Saran - चैन सिंह सारण: नागौर बोर्डिंग की छात्र संख्या बढ़ाने व कुरीति निवारण में बोर्डिंग हाउस के विद्यार्थियों ने मेलों में तथा जगमठों में जहां कहीं भी काम पड़ा चौधरी मूलचन्द सियाग (1887 - 1978) के साथ जाकर गायन व भजनों द्वारा जनता के अंधेरों रूपी पर्दे को हटाया और प्रकाश डाला जिसमें आपकी मुख्य भूमिका थी। [81]
- Divij Saran (born 2 March 1986), from Delhi, is an Indian professional tennis player. He won Gold Medal in Asian Games-2018 in Lawn tennis, Men's doubles.
- दादा भोमिया मगलू जी महाराज और जोडा़यत दादी सती (रुपा सारण) सिहाग, भोजासर बड़ा, सीकर राजस्थान (See Bhojasar Bara)
- Harlal Saharan is a BJP MLA from Rajasthan. He has been elected BJP MLA from Churu Assembly constituency in 2023. He belongs to Khasoli) village in Churu tehsil of Churu district of Rajasthan.
- Vidyadhar Saharan (Rifleman) (1950 - 10.12.1971) martyred on 10.12.1971 during Indo-Pak War-1971. He was from Ajari Khurd village in Jhunjhunu tahsil & district in Rajasthan. His statue was installed on 06.01.2019
- Unit - 7 Rajputana Rifles
- Charan Singh Saran - भोपालगढ़ तहसील के अंतर्गत कुड़ी गांव निवासी सीमा सड़क संगठन इकाई के जवान चरण सिंह सारण 24 फरवरी 2024 को अरुणाचल प्रदेश में ड्यूटी के दौरान अत्यधिक बर्फबारी में हुए एक हादसे में शहीद हो गए. जिनकी पार्थिव देह मंगलवार को कुड़ी गांव पहुंचा और यहां राज्य के सम्मान एवं गार्ड ऑफ ऑनर के साथ अंतिम संस्कार किया गया. जिसको लेकर गांव के युवा कार्यकर्ता अंतिम संस्कार में जनशालब के रूप में शामिल हुए. चरण सिंह सारण सड़क संगठन इकाई के जनरल रिजर्व इंजीनियरिंग फोर्स में सिपाही थे (भास्कर 28.02.2024)
References
- ↑ B S Dahiya:Jats the Ancient Rulers (A clan study), p.243, s.n.209
- ↑ Jat History Dalip Singh Ahlawat/Parishisht-I, s.n. स-105
- ↑ Jat History Dalip Singh Ahlawat/Parishisht-I, s.n. स-159
- ↑ Jat History Thakur Deshraj/Chapter IX,p.695
- ↑ Jat Varna Mimansa (1910) by Pandit Amichandra Sharma,p. 57
- ↑ Bhim Singh Dahiya: Jats the Ancient Rulers (A clan study)/Appendices/Appendix I, p.316
- ↑ A glossary of the Tribes and Castes of the Punjab and North-West Frontier Province By H.A. Rose Vol II/J,p.376
- ↑ Kisan Chhatrawas Bikaner Smarika 1994,pp.92-95
- ↑ Jananayak Shri Daulat Ram Saran Abhinandan Granth,p.120
- ↑ Bhim Singh Dahiya: Jats the Ancient Rulers (A clan study)/The Antiquity of the Jats,p.301
- ↑ Corpus Inscriptionium Indicarium Vol IV Part 2 Inscriptions of the Kalachuri-Chedi Era, Vasudev Vishnu Mirashi, 1955, p.450-457
- ↑ Natural History by Pliny Book VI/Chapter 18
- ↑ Ram Swarup Joon: History of the Jats/Chapter V, p. 99-100
- ↑ Ram Swarup Joon: History of the Jats/Chapter V, p. 100
- ↑ A glossary of the Tribes and Castes of the Punjab and North-West Frontier Province By H.A. Rose Vol II/J,p.376
- ↑ Jats the Ancient Rulers (A clan study)/Appendices/Appendix I,p.316
- ↑ Churu Janpad Ka Jat Itihas by Daulat Ram Saran Dalman
- ↑ Jat Express, 10 July, 2011,p.2
- ↑ Kisan Chhatrawas Bikaner Smarika 1994,p. 92
- ↑ Churu Janpad Ka Jat Itihas by Daulat Ram Saran Dalman
- ↑ Jat Express, 10 July, 2011,p.2
- ↑ Daulat Ram Saharan, Dharati Putra: Jat Baudhik evam Pratibha Samman Samaroh Sahwa, Smarika 30 December 2012, by Jat Kirti Sansthan Churu, pp.9
- ↑ Dr Naval Viyogi: Nagas – The Ancient Rulers of India, p.149
- ↑ Jananayak Shri Daulat Ram Saran Abhinandan Granth,p.120
- ↑ Churu Janpad Ka Jat Itihas by Daulat Ram Saran Dalman
- ↑ Jats the Ancient Rulers (A clan study)/The Antiquity of the Jats,p.300-301
- ↑ The Bhilsa topes: Inscriptions, P. 240
- ↑ Ram Swarup Joon: History of the Jats/Chapter V, S.No.82
- ↑ Ram Swarup Joon: History of the Jats/Chapter V, S.No.82
- ↑ Elliot, op. cit., Vol.I, p.133
- ↑ Muhammad Qasim Hindu Shah Firista, Gulsan-i-Ibrahimi, commonly known as Tarikh-i-Firishta, Nawal Kishore edition, (Kanpur, 1865), Vol.I, p.35
- ↑ Dr S.Jabir Raza, The Jats - Their Role and Contribution to the Socio-Economic Life and Polity of North and North West India. Vol I, 2004, Ed Dr Vir Singh
- ↑ Inscription No.1, Tod, op.cit., Vol.I, p. 622-23.
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Islam, vol.II, p.488
- ↑ Chachnama, pp.98, 117,131
- ↑ Zai'nul-Akhbar, p.191; Tarikh-i-Firishta, Vol.I,p.35
- ↑ Chachnama, pp.104,167
- ↑ Richard F. Burton, op. cit., p.246
- ↑ Inscription No.1, Tod, op.cit., Vol.II, Appendix pp. 914-917.
- ↑ Dr S.Jabir Raza, The Jats - Their Role and Contribution to the Socio-Economic Life and Polity of North and North West India. Vol I, 2004, Ed Dr Vir Singh
- ↑ Inscription No.II, Tod, op.cit., Vol.II, Appendix, pp. 917-919 and n. 13
- ↑ Chachnama, p.166
- ↑ Dr S.Jabir Raza, The Jats - Their Role and Contribution to the Socio-Economic Life and Polity of North and North West India. Vol I, 2004, Ed Dr Vir Singh
- ↑ Hasan Nizami, Tajul-ma'asir, Fascimile translation in ED, Vol. II, p.218
- ↑ Nainsi Khyat, Vol. I p. 12
- ↑ Dr Karni Singh (1947): The Relations of House of Bikaner with Central Power, Munsi Ram Manohar Lal Pub. Pvt, 54 Rani Jhansi Road, New Delhi.
- ↑ Dr Brahmaram Chaudhary, The Jats, Vol. 2, Ed Dr Vir Singh, Originals, Delhi, 2006, ISBN 81-88629-52-9, p. 250
- ↑ Thakur Deshraj, Jat Itihas (Hindi), Maharaja Suraj Mal Smarak Shiksha Sansthan, Delhi, 1934, 2nd edition 1992, p. 617
- ↑ Ramratna Charan, Itihas
- ↑ In praise of death: history and poetry in medieval Marwar (South Asia), By Janet Kamphorst, p.253
- ↑ A glossary of the Tribes and Castes of the Punjab and North-West Frontier Province By H.A. Rose Vol II/J,p.376
- ↑ Jats the Ancient Rulers (A clan study)/Appendices/Appendix I,p.316
- ↑ जाट वीरों का इतिहास: दलीप सिंह अहलावत, पृष्ठ.187
- ↑ दयालदास ख्यात, देशदर्पण, पेज 20
- ↑ Dr Pema Ram, The Jats Vol. 3, ed. Dr Vir Singh,Originals, Delhi, 2007 p. 209
- ↑ चौधरी हरिश्चंद्र नैन, बीकानेर में जनजाति, प्रथम खंड, पेज 18
- ↑ Dr Pema Ram, The Jats Vol. 3, ed. Dr Vir Singh,Originals, Delhi, 2007 p. 202
- ↑ Kisan Chhatrawas Bikaner Smarika 1994,pp.92-95
- ↑ Jananayak Shri Daulat Ram Saran Abhinandan Granth,p.120
- ↑ Jananayak Shri Daulat Ram Saran Abhinandan Granth,p.120
- ↑ Jananayak Shri Daulat Ram Saran Abhinandan Granth,p.120
- ↑ Dharati Putra: Jat Baudhik evam Pratibha Samman Samaroh Sahwa, Smarika 30 December 2012, by Jat Kirti Sansthan Churu, p.39
- ↑ Churu Janpad Ka Jat Itihas by Daulat Ram Saran Dalman
- ↑ Kisan Chhatrawas Bikaner Smarika 1994,pp.92-95
- ↑ Jananayak Shri Daulat Ram Saran Abhinandan Granth,p.120
- ↑ Jananayak Shri Daulat Ram Saran Abhinandan Granth,p.120
- ↑ saharanparivar
- ↑ Jananayak Shri Daulat Ram Saran Abhinandan Granth,p.120
- ↑ A study of the Bhagavata Purana; or, Esoteric Hinduism by Purnendu Narayana Sinha, p. 223
- ↑ https://www.jatland.com/forums/showthread.php/40442-गोत्र-जोड़ने-बाबत
- ↑ James Tod: Annals and Antiquities of Rajasthan, Volume II, Annals of Jaisalmer, p.204
- ↑ Thakur Deshraj:Jat Jan Sewak, 1949, p.146-147
- ↑ Thakur Deshraj:Jat Jan Sewak, 1949, p.189
- ↑ Thakur Deshraj:Jat Jan Sewak, 1949, p.201
- ↑ Thakur Deshraj: Jat Jan Sewak, 1949, p.209
- ↑ Thakur Deshraj: Jat Jan Sewak, 1949, p.209
- ↑ Thakur Deshraj: Jat Jan Sewak, 1949, p.209
- ↑ Uddeshya: Sarv Samaj Baudhik evam Pratibha Samman Samaroh Churu, Smarika, June 2013, by Jat Kirti Sansthan Churu,p.192
- ↑ Jat Gatha, September-2015,p. 15
- ↑ Jat Gatha, September-2015,p. 15
- ↑ Thakur Deshraj:Jat Jan Sewak, 1949, p.185
- Thakur Deshraj: Jat Itihas (Hindi), Maharaja Suraj Mal Smarak Shiksha Sansthan, Delhi, 1934.
- James Tod: Annalas and Antiquities of Rajasthan (1829)
Back to Gotras / Jat Kingdoms in Ancient India
- Jat Gotras
- Ancient Jat Gotras
- The Mahabharata Tribes
- Gujarat
- Rajasthan
- Haryana
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
- Punjab
- Gotras in Sikar
- Gotras in Churu
- Gotras in Hanumangarh
- Gotras in Ganganagar
- Gotras in Jhunjhunu
- Gotras in Jodhpur
- Gotras in Barmer
- Gotras in Nagaur
- Gotras in Bikaner
- Gotras in Jalor
- Gotras in Pali
- Gotras in Dausa
- Gotras in Jaipur
- Gotras in Tonk
- Gotras in Ajmer
- Gotras in Bhilwara
- Gotras in Sirohi
- Gotras in Banas Kantha
- Gotras in Yamunanagar
- Gotras in Fatehabad
- Gotras in Bhopal
- Gotras in Harda
- Gotras in Raisen
- Gotras in Rampur
- Gotras in Khargone
- Gotras in Mandsaur
- Gotras in Nimach
- Gotras in Ratlam
- Gotras in Sehore
- Gotras in Dewas
- Gotras in Dhar
- Gotras in Barwani
- Gotras in Ujjain
- Gotras in Indore
- Gotras in Kaithal
- Gotras in Sirsa
- Gotras in Bhiwani
- Gotras in Rohtak
- Gotras in Hisar
- Gotras in Kurukshetra
- Gotras in Muzaffarnagar
- Gotras in Meerut
- Gotras in Bijnor
- Gotras in Saharanpur
- Gotras in Hapur
- Gotras in Ludhiana
- Jat Kingdoms in Ancient India
- Genealogy
- Bard History
- Bhati History
- Jat History
- Yaduvanshi